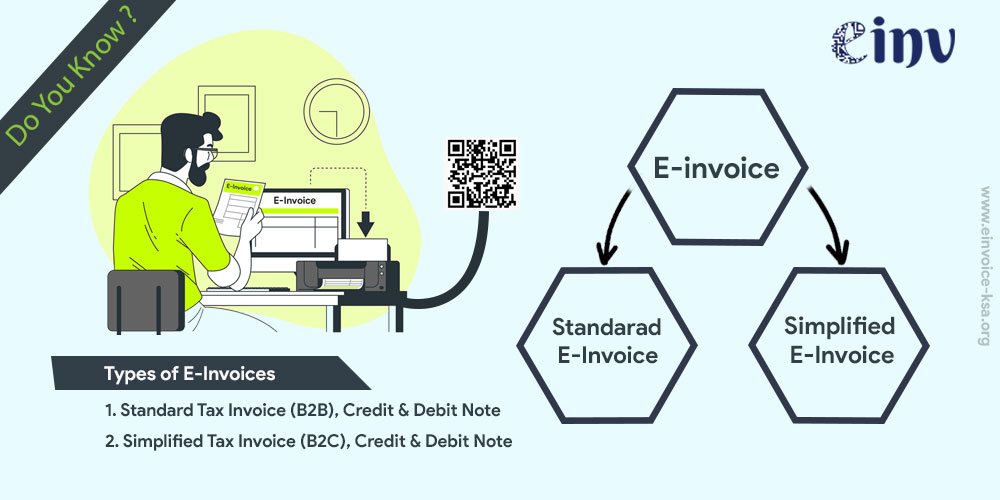
Types of E – Invoices.
- Standard Invoice: Invoice which has Tax information of Vendor & Customer Both (B2B)
- Simplified Invoice: Invoice which has Tax information of vendor only, Not Customer (B2C)
- Tax e-invoice (Standard e-invoice)
In order for consumers to be eligible for a claim VAT deduction under the VAT Implementing Regulations, both Businesses to Government (B2G) as well as Business to Business (B2B) transactions need to include a standard e-invoice. These invoices should be presented by vendors in a manner that is officially authorized by the government.
Standard invoices cannot be issued beginning in January 2023 until they have been validated and signed by the Fatoora portal as part of its association via the ZATCA portal. VAT legislation asks for information like seller or buyer details, transaction information, and technical information, which must be included in all standard e-invoices.
If a buyer is VAT registered, will have to add their VAT registration number to the invoice, and can opt to add a QR code.
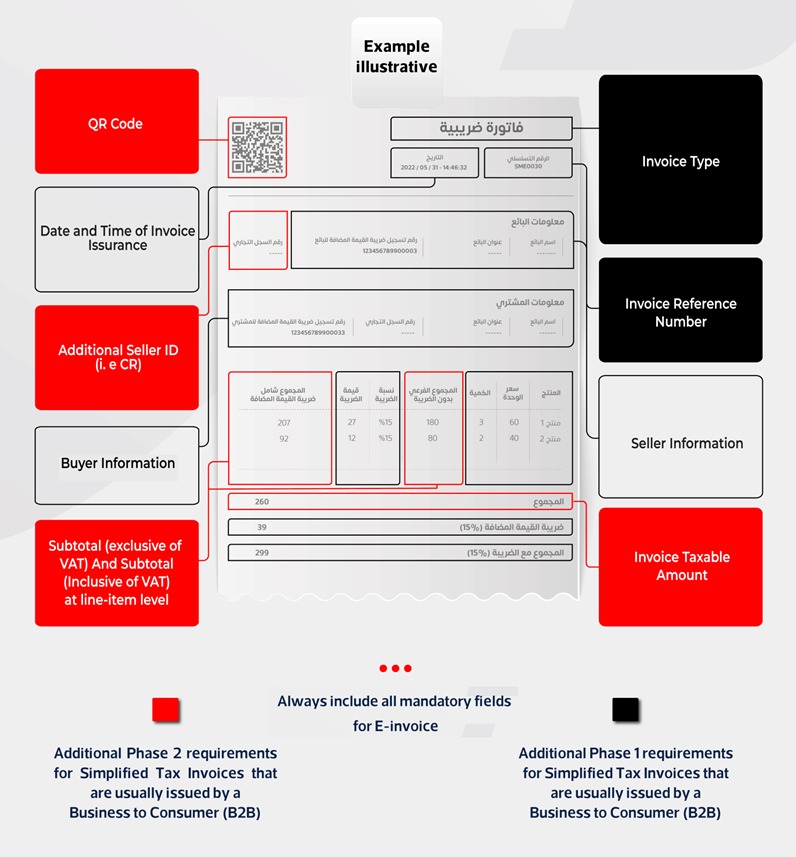
What standard E invoice includes:
- Applicable For: B2B transactions where both parties are VAT registered businesses, and the taxable supply value exceeds SAR 3,000 (excluding VAT).
-
Content: Contains all mandatory data elements specified by ZATCA, including details like:
- Seller and buyer information
- Invoice number and date.
- Product/service description
- Quantity and unit price
- VAT amount
- Taxable amount
- QR code with encrypted data
- Digital signature (optional)
- Format: XML or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML)
- Benefits: Provides detailed information for tax purposes and record-keeping.
- Limitations:
- Complexity: Requires more data and fields compared to simplified versions, potentially increasing creation time and complexity.
- Not Ideal for Small Transactions: Can be overkill for low-value transactions where detailed information isn't crucial.
- Technical Requirements: Integration with accounting systems and compliance with regulations might require technical expertise.
Format of the Standard E invoice is shown Below:
- Simplified e-invoices
In KSA, a simplified tax invoice is prepared and kept in a structured electronic format and is often issued for a B2C (business to consumer) transaction. It does not typically include the buyer's information. Simplified Tax Invoices may also be produced for business-to-business transactions if the supply value is less than SAR 1,000.
In making a simplified tax invoice, the customer does not require an invoice for VAT deduction purposes using simplified e-invoices. The information listed in Article 53(8) of the VAT Implementing Regulations and e-Invoicing Resolution should be included in the e-invoice for Business to Customer B2C transactions.
Customers should receive a streamlined e-invoice at the moment of sale, and an extra copy of the invoice must be stored and kept on file. Taxpayers are only required to provide an electronic invoice in the first phase. But taxpayers must report the streamlined e-invoice in the second phase on the ZATCA portal within 24 hours of its issuance.
What Simplified E invoice includes:
- Applicable For: Transactions involving non-taxable entities or taxable supplies with a value less than SAR 3,000 (excluding VAT).
-
Content: Includes essential information like:
- Seller and buyer information
- Invoice number and date.
- Product/service description
- Total amount (including VAT)
- QR code with essential data
- Format: XML or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML)
- Benefits: Offers a lighter structure for simpler transactions.
- Limitations:
- Limited Data: Lacks detailed information essential for complex transactions or tax purposes.
- Not Universally Accepted: Some businesses or countries might not accept simplified e-invoices due to insufficient data.
- Potential Reconciliation Issues: Limited information could lead to challenges in reconciling invoices with accounting records.
Format of the Simplified E invoice is shown Below:
Invoice Type Code
Invoice Type Code in XML
UBL contains a list of values contained in UN/CEFACT code list 1001 to indicate the document type. The UBL document types that reflect the types defined in KSA VAT Law are Invoice, Debit note, Credit note, and Self-billed invoice. However, KSA VAT Law also requires defining a Simplified Tax Invoice. To indicate Simplified Tax Invoice the standard UBL attribute “name” is defined, and the first two characters of this attribute differentiate between Tax Invoice, Simplified Tax Invoice, and other types of documents.
Additional flags indicating transaction type have been added as the final four positions in the “name” attribute (see Invoice transaction code in the table below).
The valid invoice type codes for Saudi Arabia electronic invoice are listed in the table below:
NOTE on UN/EDIFACT code list 1001 compliance:
-
For Tax Invoice, code is 388 and subtype is 01. ex. <cbc:InvoiceTypeCode name=”0100000”>388
</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode> - For Simplified Tax Invoice, code is 388 and subtype is 02. ex. <cbc:InvoiceTypeCode name=”0200000”>388</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode>
- For Tax invoice debit note, code is 383 and subtype is 01. ex. <cbc:InvoiceTypeCode name=”0100000”>383</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode>
- For Simplified debit note, code is 383 and subtype is 02. ex. <cbc:InvoiceTypeCode name=”0200000”>383</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode>
- For Tax invoice credit note, code is 381 and subtype is 01. ex. <cbc:InvoiceTypeCode name=”0100000”>381</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode>
- For Simplified credit note, code is 381 and subtype is 02. ex. <cbc:InvoiceTypeCode name=”0200000”>381</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode>
- For Prepayment Tax Invoice, code is 386 and subtype is 01. ex. <cbc:InvoiceTypeCode name=”0100000”>386</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode>
- For Prepayment Simplified Tax Invoice, code is 386 and subtype is 02. ex. <cbc:InvoiceTypeCode name=”0200000”>386</cbc:InvoiceTypeCode>
Request A Call Back
We will try and understand your system architecture & discuss details of what it will take for you to get 100% compliant.